Co-infection with 'superbug' spikes Covid virus replication by 15-fold
By IANS | Published: March 21, 2023 05:09 PM2023-03-21T17:09:03+5:302023-03-21T17:25:17+5:30
Toronto, March 21 Researchers have identified a protein found in superbugs that enhances SARS-CoV-2 replication by 10- to ...
Co-infection with 'superbug' spikes Covid virus replication by 15-fold
Toronto, March 21 Researchers have identified a protein found in superbugs that enhances SARS-CoV-2 replication by 10- to 15-fold.
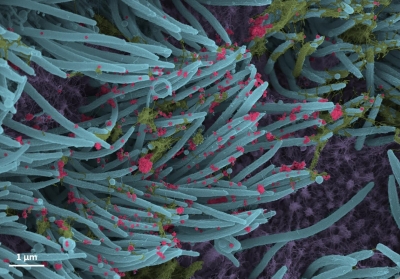
Global data shows nearly 10 per cent of severe Covid-19 cases involve a secondary bacterial co-infection with Staphylococcus aureus, also known as staph A, being the most common organism responsible for co-existing infections with SARS-CoV-2.
The study, published in the journal iScience, revealed that the addition of a "superbug" methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) into the mix could make the Covid-19 outcome even more deadly.
While the mystery of how and why the combination of these two pathogens contributes to the severity of the disease remained unsolved, the researchers identified a protein IsdA found in all strains of staph A which boosts SARS-CoV-2 replication by 10- to 15-fold.
The findings of this study are significant and could help inform the development of new therapeutic approaches for Covid-19 patients with bacterial co-infections.
Interestingly, the study also showed that SARS-CoV-2 did not affect the bacteria's growth. This was contrary to what the researchers had initially expected.
"We started with an assumption that SARS-CoV-2 and hospitalisation due to Covid-19 possibly caused patients to be more susceptible to bacterial infections which eventually resulted in worse outcomes," said Mariya Goncheva, Professor of biochemistry and microbiology at the University of Victoria.
Goncheva said bacterial infections are most commonly acquired in hospital settings and hospitalisation increases the risk of co-infection.
Disclaimer: This post has been auto-published from an agency feed without any modifications to the text and has not been reviewed by an editor
Open in app